Search This Supplers Products:RFID ReadersBarcode ScannersMobile ComputersRFID BarCode Solutions
What is RFID technology?
What is RFID technology?
RFID technology actually refers to radio frequency technology. Its technology mainly relies on the principle of magnetic field or electromagnetic field to realize two-way communication between devices through wireless radio frequency, thereby realizing the function of exchanging data. The biggest feature of this technology is that it can obtain the other information party without contact.
ETC, logistics, and libraries are some typical application scenarios. Commonly used radio wave bands for RFID technology mainly include: low frequency, high frequency, ultra-high frequency and microwave frequency bands.
RFID system composition
The RFID system mainly consists of three parts: reader/writer, electronic tag and data management system.
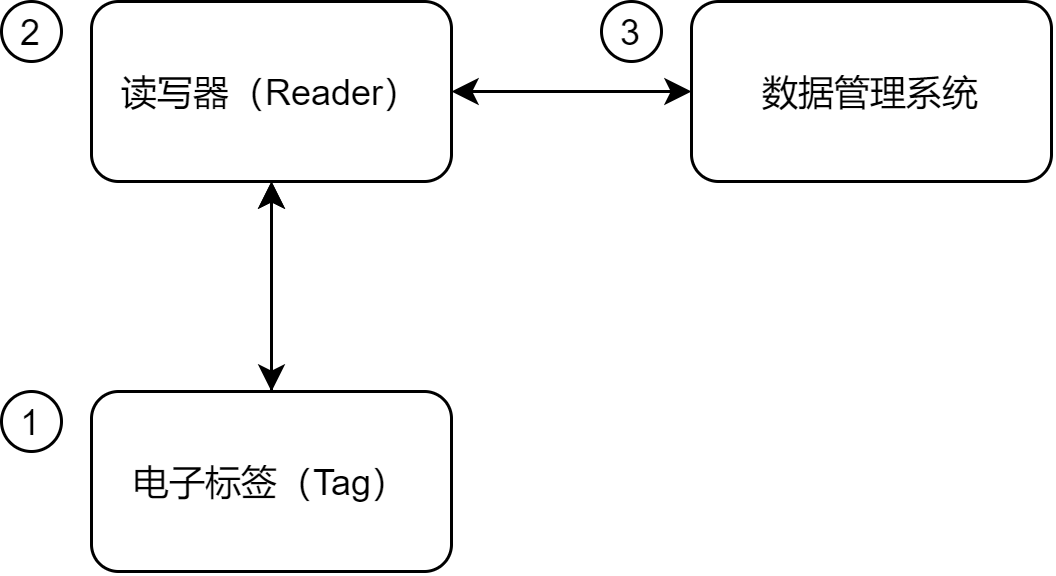
Reader: Also called a reader, it is a device mainly used to read out the information in electronic tags or write the information required by the tag into the tag. According to different uses, readers are divided into read-only readers and read/write readers, which are the information control and processing center of the RFID system. When the RFID system works, the reader sends radio frequency energy within an area to form an electromagnetic field. The size of the area depends on the transmission power. Tags in the reader coverage area are triggered, send the data stored in them, or modify the data stored in them according to the instructions of the reader and can communicate with the computer network through the interface.

Electronic tag (Tag): Electronic tag is mainly used to store certain data information. At the same time, it will receive signals from the reader and send the required data back to the reader. Electronic tags are generally affixed or fixedly installed on items.

Data management system: The main job is to process the electronic tag data transmitted by the reader for analysis, and at the same time complete the functions required by the user.
How RFID systems work
The working principle of the RFID system: When the electronic tag is within the recognition range of the reader, the reader emits radio wave energy of a specific frequency. The electronic tag will receive the radio frequency signal emitted by the reader and generate an induced current. Using the energy generated by this current, the electronic tag sends out the information stored in its chip.
How RFID systems work
This type of electronic tag is generally called a passive tag or passive tag, or the tag actively sends a signal of a certain frequency to the reader. This type of electronic tag is generally called an active tag or active tag. After the reader receives the information returned by the electronic tag, it decodes it and then sends it to the relevant application software or data management system for data processing. RFID classification RFID technology can be divided into three categories based on the power supply method of its tags, namely passive RFID, active RFID and semi-active RFID.
1.Passive RFID
The passive RFID system obtains energy from the electromagnetic induction coil to supply itself with short-term power and complete information exchange. It has a simple structure, low cost, low failure rate and long service life. However, the effective identification distance of passive RFID is usually shorter and is generally used for short-range contact identification. Passive RFID mainly works in the lower frequency bands of 125kHz, 13.56MHz, etc. Typical applications of passive RFID systems include: bus cards, second-generation ID cards, canteen meal cards, etc.
2.Active RFID
The research and development of active RFID systems started late, but it has been applied in various fields. For example, ETC uses an active RFID system. Active RFID is powered by an external power supply or a built-in battery and actively sends signals to the reader, thus having a longer transmission distance and faster transmission speed. Active RFID tags can establish data communication with readers within a range of 100m, and the reading rate can reach 1700 times/s. Active RFID mainly works in ultra-high frequency bands and microwave frequency bands such as 900MHz, 2.45GHz, and 5.8GHz, and has the function of identifying multiple tags at the same time. The above characteristics of active RFID systems make them widely used in high-performance, large-scale RFID scenarios.
3.Semi-active RFID
Semi-active RFID has a short effective recognition range due to the passive RFID system; active RFID has a long enough recognition range, but requires an external power supply or built-in battery and is larger. In order to solve this contradiction, semi-active RFID systems came into being. Semi-active RFID technology is also called low-frequency activation trigger technology. Under normal circumstances, semi-active RFID tags are in a dormant state and only power the part of the tag that holds data, so they consume less power and can last for a longer time. When the tag enters the recognition range of the RFID reader, the reader first uses a 125kHz low-frequency signal to accurately activate the tag in a small range to enter the working state, and then transmits information to it through 2.4GHz microwaves. In other words, multiple low-frequency readers are placed at different locations to activate semi-active RFID products, thereby achieving both positioning and data collection and transmission.
To realize RFID asset management, you can consider using NB-IOT or Lora technology to transmit the data collected by the RFID reader to the Lora base station in real time and upload it to the backend. At present, we understand that some companies are already trying, using RFID for identification and NB or Lora for transmission. If you develop it yourself, you need to do the hardware docking and data docking, and then do the backend. There should be mature hardware solutions on the market, but the software backend definitely needs to be developed by yourself. Generally, hardware companies will provide SDKs. At present, RFID is widely used, involving all aspects of social life. It can be applied in logistics, retail, manufacturing, clothing industry, medical care, identity recognition, anti-counterfeiting, asset management, transportation, food, automobiles, military, financial payment and other fields. PFID technology It should be a very promising development direction.
