Search This Supplers Products:RFID ReadersBarcode ScannersMobile ComputersRFID BarCode Solutions
What are the applications of RFID technology in smart manufacturing?
What are the applications of RFID technology in smart manufacturing?

Since the popularization of RFID technology, RFID has been used in a wide range of applications. Initially, it was mainly used in logistics. However, since its development, RFID applications can be seen in retail, logistics, transportation, medical care, manufacturing, etc. Although RFID technology is no longer a new technology, with the advent of the smart era, the industry has continued to develop various RFID application scenarios based on market demand in recent years. In the case of smart manufacturing, in view of the demand for resources and improved cost efficiency, manufacturers have also begun to adopt RFID technology to achieve applications such as real-time location tracking, asset or personnel monitoring, process control on production lines, and supply chain management. Let's take a look at the applications of RFID technology in smart manufacturing.
1. Application of RFID technology in smart products
RFID technology combined with smart boards can realize full-cycle information management from design, production, sales, inspection, diagnosis and maintenance, information statistics, scrapping, operation information record feedback, diagnosis and analysis. It is of great value to enhance the intelligent image of products and realize the intelligentization of products throughout their life cycle.
2. Application of RFID technology in smart logistics
(1) Supply chain vehicle guidance and unloading management
Through RFID technology, combined with the material supply needs of the factory area, it can realize the reservation, queuing, identification of factory supplier vehicles, and intelligent allocation of unloading resources in the factory area. Just like the bus ticket booking system, before arriving at the station (factory), the supplier makes an appointment and queues (purchases tickets) through the online appointment system. After arriving at the factory (station), follow the signs to the reserved unloading space to unload (wait and get on the bus) ).
Currently, the Malong base of a well-known domestic brand of microwave ovens has implemented a material-pull supply chain model by deploying and implementing a supply chain vehicle guidance and unloading management system. Through the RFID system, we can understand the status of logistics resources in the entire factory area, channelize the logistics resources in the factory area, realize the entry time of supply chain vehicles into the factory, unloading resource arrangement guidance and time control, and improve the utilization rate of logistics resources in the factory area. Through the unified deployment and guidance of vehicles and unloading resources in the factory area, the factory has increased the utilization rate of logistics resources to more than 30%, and the delivery accuracy has increased to more than 15%.

(2) Material distribution turnover box management
The application of RFID technology to logistics turnover box management can greatly improve the operating efficiency of the logistics system and realize digital warehousing management (warehousing location management, rapid real-time inventory), etc., making management more scientific, timely and effective, and ensuring high-quality data exchange in the supply chain. This will bring about a significant improvement in logistics efficiency, thereby reducing the overall cost of the system.
In Factory Building No. 18 of a state-owned enterprise, Honglu RFID readers are installed at all material distribution outlets, and RFID pickers are installed beside the assembly line. All material incoming and outgoing and line-side picking information will be collected in a timely manner and fed back to the backend system. The intelligent identification system for palletizing warehouses can realize transparency and intelligent guidance of the distribution process through intelligent components such as automatic warehouses, RFID smart trolleys, and RFID pallets, and improve the efficiency and accuracy of assembly material distribution.
3. Application of RFID technology in smart workshops
(1) Tool life cycle management and control
As we all know, the purpose of tool management and control is to realize the information management of the tool life cycle and to understand the use and inventory status and location of the tool in a timely manner. Before the tools are purchased and stored in the warehouse, RFID electronic tags are installed on the tools as the unique identification information of the tools. During the scheduling and use of tools, by collecting tool information in a timely manner through RFID reading and writing equipment, you can clearly understand in the system whether the tool has been loaded, the specific corresponding machine tool, and the cycle and duration of use. By tracking the position and usage status of the cutting tools in a timely manner, companies can promptly understand the wear and tear of the cutting tools and replace them to ensure the safety of the cutting tools.
A domestic heavy-duty machine tool company uses an RFID reader to promptly collect machine tool RFID tag information to understand tool usage status data, and promptly replaces tools based on the tool wear status feedback system. Improve the safety of tool use and ensure that machine tool processing production efficiency is at its most efficient state.

(2) Production line mixed flow manufacturing
With the growth of users' personalized needs, selection and customization have gradually become a trend in the industrial production of manufacturing companies. The mixed assembly line production model of mixed flow manufacturing can well meet the personalized customized selection production needs. Mixed flow manufacturing is a production method in which enterprises produce multiple products on one assembly line within a certain period of time. Several product varieties with basically the same process flow and production operation methods are scientifically arranged and put into production on an assembly line in a rhythmic and proportional manner. Mixed continuous flow production is based on a comprehensive balance of variety, output, working hours, and equipment load.
By installing RFID electronic tags on complex parts and pallets, and installing RFID industrial readers and writers on processing equipment and lines, intelligent communication between products and equipment is achieved, effectively avoiding many problems such as chaotic process management caused by untimely data collection. Provide data support for MES through timely collection of work-in-progress status and production process status, ensuring that MES can timely produce and schedule each workstation. Keep each workstation busy in a cycle to complete the maximum amount of operations, thereby reducing idle time and improving productivity.
At present, an automobile company has installed RFID tags on the cylinder block and head processing production line to achieve the mixed-flow production of more than 6 types of cylinder blocks. The quality data and process data of the entire production line are effectively collected. A certain brand of home air conditioners installed RFID tags on the factory's flexible assembly lines, processes, and work boards to automatically collect data during the home appliance assembly process, increasing the data collection rate to 99%. Manual barcode scanning events are reduced by 5 minutes for a single product on each line, and the MES data accuracy rate is increased to 90%.
(3) Intelligent mold maintenance management
A company in Dongguan that focuses on the production of electrode tubes has improved CNC processing efficiency, reduced warehouse personnel, reduced measuring personnel, and increased EDM utilization by more than 20% by opening up the information flow and manufacturing flow from mold design to manufacturing.
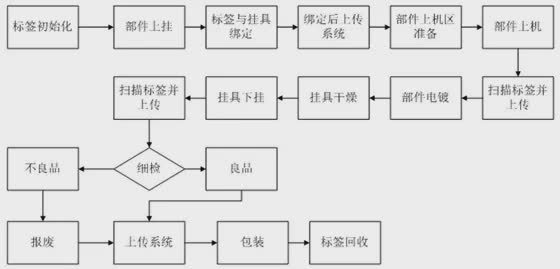
The specific implementation method is to install RFID tags on each electrode tube to control the entire process of transistor storage, production, measurement and discharge. Through the collection of inventory, configuration, and on-site data, it extends from the design of the electrode to the entire process of manufacturing, measurement, and use, allowing data and manufacturing to interact seamlessly, realizing automation and unmanned operation of the entire process.
With the development of the Internet of Things, intelligent production has gradually made breakthroughs, which have brought great benefits to intelligent manufacturing by improving product quality, improving production efficiency, and subverting inherent thinking. An intelligent clothing production line only takes 22 seconds to produce a piece of clothing, and a production line can be operated independently by only one worker, so the production line can produce about 800,000 pieces of clothing a day. This data was completely unimaginable before, but now it has been achieved.
