Search This Supplers Products:RFID ReadersBarcode ScannersMobile ComputersRFID BarCode Solutions
How will RFID technology work in libraries?
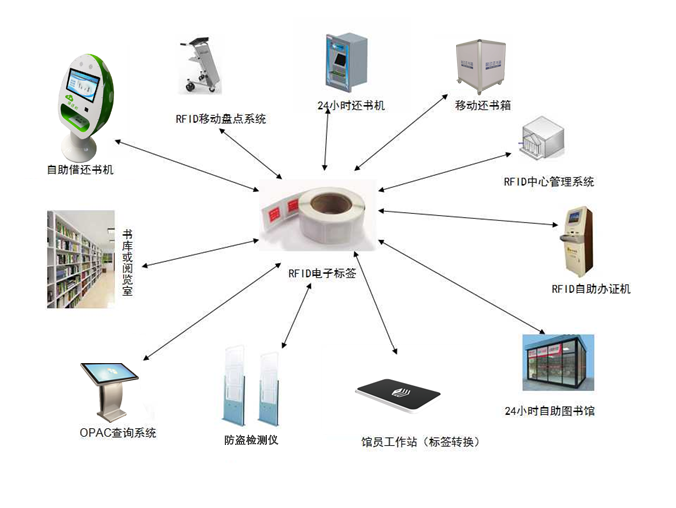
RFID technology revolutionizes library operations by enabling rapid book identification, automated borrowing and returning, efficient inventory management, and theft prevention, thereby streamlining processes and enhancing patron satisfaction.
1.Automated Borrowing and Returning:
RFID tags attached to books allow for non-contact, simultaneous identification of multiple books.
Patrons can self-checkout and return books quickly by placing them on RFID-enabled machines, reducing wait times and staff workload.
2.Efficient Inventory Management:
RFID technology facilitates rapid book counting and shelf-checking with handheld scanners or smart shelves, reducing the time and labor required for traditional inventory methods.
It enables real-time updates on book locations, improving accessibility and reducing misplaced books.
3.Theft Prevention:
RFID-based security gates detect unauthorized books exiting the library, triggering alarms and deterring theft.
This enhances security and protects library assets.
4.Enhanced User Experience:
The autonomy provided by self-service machines increases patron satisfaction and privacy.
RFID technology also supports advanced services like location-based book recommendations and navigation systems, enhancing the overall library experience.
5.Data-Driven Decision Making:
RFID systems collect data on book circulation, patron behavior, and inventory status, providing valuable insights for library management and resource allocation.
Conclusion:
By leveraging RFID technology, libraries can achieve significant improvements in operational efficiency, security, and patron satisfaction. This technology underpins the transformation towards smarter, more accessible, and user-centric library services.