Search This Supplers Products:RFID ReadersBarcode ScannersMobile ComputersRFID BarCode Solutions
How To Choose A Suitable RFID Frequency For Your Application
time2022/02/18

- How to choose a suitable RFID frequency for your application? With the rapid development of RFID applications, RFID tags and readers need to be tuned to the same frequency before they can communicate. There are generally 3 types of RFID frequencies, namely low frequency (LF), high frequency (HF) and ultra high frequency (UHF).
- How To Choose A Suitable RFID Frequency For Your Application
- The application of RFID is developing rapidly. Some sensor monitoring is widely used in some applications such as logistics and healthcare.
- Sensor monitoring can collect and send relevant data through RFID, including temperature, humidity, movement, etc.
- At the same time, it is similar to the radio, which must be tuned to a specific frequency to hear different channels. The RFID tag and the reader must be tuned to the same frequency to communicate.
- There are generally 3 types of RFID frequencies:
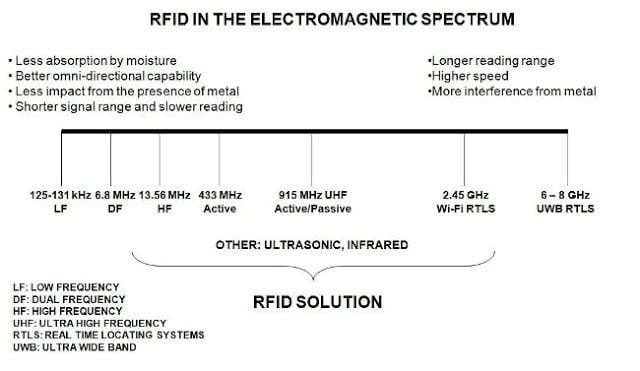
- Low Frequency (LF), 125 – 134 kHz
- High Frequency (HF), 13.56 MHz
- Ultra High Frequency (UHF), 433 and 860-960 MHz
- Low Frequency (LF)
- Low frequency tags have longer wavelengths and are able to penetrate thin metal substances more efficiently.
- In addition, low-frequency RFID systems are suitable for reading objects with high water content, such as fruit or beverages, but have a limited reading range of centimeters or inches.
- Some common examples are access control systems and animal tags.
- High Frequency (HF)
- High-frequency tags can be used for detection of metal objects, as well as goods and objects with moderate moisture content.
- Typically, high-frequency RFID systems have a read range in the range of a few inches, but can have a maximum read range of about three feet (1 meter). Typical high frequency RFID applications include tracking library books.
- Ultra High Frequency (UHF)
- Compared to LF and HF, UHF generally provides better read range (can be as far as 50+ feet, but depends on RFID system settings) and has a faster transfer data rate, i.e. can read more Label.
- However, because UHF radio waves have shorter wavelengths, their signals are more easily attenuated, and they cannot pass through metal or water.
- Due to its high data transfer rate, UHF RFID tags are ideal for connecting many items at one time, such as cargo boxes. In addition, because UHF RFID has a longer reading range, it is suitable for some UHF RFID applications, such as electronic toll collection and parking lot access control.

